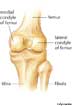
condyle
Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
Related to condyle: mandibular condyle
con·dyle
(kŏn′dīl′, -dl)n.
A rounded prominence at the end of a bone, most often for articulation with another bone.
[Latin condylus, knuckle, from Greek kondulos.]
con′dy·lar (-də-lər) adj.
con′dy·loid′ (-dl-oid′) adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
condyle
(ˈkɒndɪl)n
(Anatomy) the rounded projection on the articulating end of a bone, such as the ball portion of a ball-and-socket joint
[C17: from Latin condylus knuckle, joint, from Greek kondulos]
ˈcondylar adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
con•dyle
(ˈkɒn daɪl, -dl)n.
1. the rounded process at the end of a bone, forming part of a joint.
2. (in arthropods) a similar process formed from the hard integument.
[1625–35; < New Latin condylus knuckle < Greek kóndylos]
con′dy•lar, adj.
con′dy•loid`, adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
con·dyle
(kŏn′dīl′) A rounded prominence at the end of a bone.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. |  condyle - a round bump on a bone where it forms a joint with another bone condyle - a round bump on a bone where it forms a joint with another boneappendage, outgrowth, process - a natural prolongation or projection from a part of an organism either animal or plant; "a bony process" condylar process, condyloid process, mandibular condyle - the condyle of the ramus of the mandible that articulates with the skull lateral condyle - a condyle on the outer side of the lower extremity of the femur medial condyle - a condyle on the inner side of the lower extremity of the femur |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
condylus
con·dyle
n. cóndilo, porción redondeada de un hueso, usualmente en la articulación.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
condyle
n cóndiloEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.