nucleolus
(redirected from nucleoli)Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia.
nu·cle·o·lus
(no͞o-klē′ə-ləs, nyo͞o-)n. pl. nu·cle·o·li (-lī′)
A small body in the nucleus of a cell that contains protein and RNA and is the site for the synthesis of ribosomal RNA and for the formation of ribosomal subunits.
[New Latin, from Latin, diminutive of nucleus, kernel; see nucleus.]
nu·cle′o·lar (-lər) adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
nucleolus
(ˌnjuːklɪˈəʊləs)n, pl -li (-laɪ)
(Biology) a small rounded body within a resting nucleus that contains RNA and proteins and is involved in the production of ribosomes. Also called: nucleole
[C19: from Latin, diminutive of nucleus]
ˌnucleˈolar, ˈnucleoˌlate, ˈnucleoˌlated adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
nu•cle•o•lus
(nuˈkli ə ləs, nyu-)n., pl. -li (-ˌlaɪ)
a small, rounded body within the cell nucleus, functioning in ribosome manufacture.
nu•cle′o•lar, adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
nu·cle·o·lus
(no͞o-klē′ə-ləs) A usually round structure located in the nucleus of a cell and involved in the formation of ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis in cells.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. | 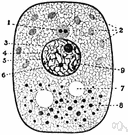 nucleolus - a small round body of protein in a cell nucleus; such organelles contain RNA and are involved in protein synthesis nucleolus - a small round body of protein in a cell nucleus; such organelles contain RNA and are involved in protein synthesiscell nucleus, karyon, nucleus - a part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction cell organ, cell organelle, organelle - a specialized part of a cell; analogous to an organ; "the first organelle to be identified was the nucleus" |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
nu·cle·o·lus
n. nucléolo, pequeña estructura esférica en el núcleo celular.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012