rhizome
(redirected from Rhizomes)Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia.
rhi·zome
(rī′zōm′)n.
A horizontal, usually underground stem that often sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Also called rootstock.
[Greek rhizōma, mass of roots, from rhizoun, to cause to take root, from rhiza, root; see wrād- in Indo-European roots.]
rhi·zom′a·tous (-zŏm′ə-təs, -zō′mə-) adj.
rhi·zom′ic adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
rhizome
(ˈraɪzəʊm)n
(Botany) a thick horizontal underground stem of plants such as the mint and iris whose buds develop new roots and shoots. Also called: rootstock or rootstalk
[C19: from New Latin rhizoma, from Greek, from rhiza a root]
rhizomatous adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
rhi•zome
(ˈraɪ zoʊm)n.
a rootlike underground stem, commonly horizontal in position, that usu. produces roots below and sends up shoots progressively from the upper surface.
[1835–45; < New Latin rhizoma < Greek rhízōma root, stem = rhizō-, variant s. of rhizoûn to fix firmly, take root (derivative of rhíza root1) + -ma n. suffix of result]
rhi•zom′a•tous (-ˈzɒm ə təs, -ˈzoʊ mə-) adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
rhi·zome
(rī′zōm′)The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. | 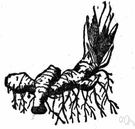 rhizome - a horizontal plant stem with shoots above and roots below serving as a reproductive structure rhizome - a horizontal plant stem with shoots above and roots below serving as a reproductive structure |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
oddenek
maavarsi
rizóma
Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
rhizome
n → Rhizom nt, → Wurzelstock m
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995

